1. Robbery, that is, the open theft of someone else’s property, is punishable by compulsory labor for a term of up to four hundred eighty hours, or correctional labor for a term of up to two years, or restriction of liberty for a term of two to four years, or forced labor for a term of up to four years. , or arrest for a term of up to six months, or imprisonment for a term of up to four years.
2. Robbery committed: a) by a group of persons by prior conspiracy; b) the clause became invalid on December 11, 2003 - Federal Law of December 8, 2003 N 162-FZ; c) with illegal entry into a home, premises or other storage; d) using violence that is not dangerous to life or health, or with the threat of using such violence; e) on a large scale - is punishable by forced labor for a term of up to five years, or by imprisonment for a term of up to seven years, with or without a fine in the amount of up to ten thousand rubles or in the amount of the wages or other income of the convicted person for a period of up to one month, and with restriction of freedom for a term of up to one year or without it.
3. Robbery committed: a) by an organized group; b) on an especially large scale, - c) the clause became invalid on December 11, 2003 - Federal Law of December 8, 2003 N 162-FZ - punishable by imprisonment for a term of six to twelve years with a fine of up to one million rubles or in the amount of wages or other income of the convicted person for a period of up to five years or without it and with restriction of freedom for a period of up to two years or without it.
Robbery, theft or robbery?
1. Robbery is a crime in which the offender steals the property of the owner in front of his eyes (or in the presence of third parties) and does not cause any violence. Or the violence does not threaten the health of the victim. This type of crime is regulated by Article 161 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
The intention of the attacker matters - if he did not know that he was being seen, it is still considered theft. And if he knew, then it was robbery.
The main factors for qualifying a crime as “robbery” are:
- unlawful entry into the premises, etc.;
- openness of property theft; the crime is committed in full view of the owner of the property or other people;
- the observers present, like the criminal himself, understand the illegality of the actions taken by the attacker;
- absence of violence or violence that does not pose a threat to the health and life of the victim;
- the possession of other people's property arises from selfish desire.
2. If a criminal steals property secretly, trying not to show himself, etc., then this type of crime is called theft .
3. If a criminal steals materially valuable property, using violence for such purposes that poses a threat to the health of another person (or threatens to use this type of violence), this is considered robbery . Otherwise, the classification of the crime is identical to robbery.
The corpus delicti of “robbery” is always material (economic and legal value is also important). Its goal is to seize someone else's property into one's own property against the will of the victim.
In this video, the lawyer talks about the classification of crimes of theft (theft, robbery, robbery). The features and composition of each type of crime are touched upon.
The robbery is considered completed from the moment
As a general rule, robbery is considered completed from the moment when the guilty person has a real opportunity to use the stolen property at his own discretion, even if he did not have time to use it.
When qualifying crimes of this kind, as a rule, many controversial issues arise, because robbery can easily be confused with other similar crimes - theft or robbery, and the investigation does not always want to understand in detail all the nuances of the case. Therefore, immediately after initiating a criminal case, you should contact a qualified lawyer. The specialist will carefully analyze all the materials and suggest how you can get out of the current situation with the least losses.
If you are an injured party, the lawyer will give you a sample statement and help you correctly state the essence of your claims, selecting the necessary evidence and arguments.
Types of robbery
The crime of robbery has many varieties. Let's look at them all:
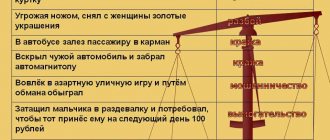
- Robbery of other people's property. The most standard type of crime, has no special distinctive features.
- Violent robbery . A crime committed with the use or threat of violence. If the injuries received by the victim exceed the category of “minor harm to health,” this type of crime smoothly develops into robbery.
- Robbery . A crime with elements of robbery. The criminal may threaten violence and display a firearm, although in reality it will be a pneumatic weapon, etc.
- Robbery with murder. The totality of liability for two crimes at once - robbery and robbery:
– if the murder was intentional – Article 105 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation;
– if due to negligence – Article 111 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
- Robbery as part of a group, by agreement with a criminal bias. Usually occurs on a significant scale: apartments, banks, museums, etc.
- Assault for the purpose of robbery. This implies lightning-fast actions on the part of the attacker: knock him down, take away valuables and escape from the scene of the crime as quickly as possible.
- Attempted robbery. When an attacker committed a crime with the intention of robbing, but received a rebuff from the victim or was unable to complete the robbery for other reasons beyond his control. Qualifies under Part 3 of Article 30 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation and Part 1 of Article 161 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
What is a completed crime?
In accordance with Part 1 of Art. 29 of the Criminal Code, a criminal act can be called completed if it contains all the elements of a crime provided for by the norms of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
In general, a completed crime is characterized by the complete realization of the criminal intentions of the offender, expressed in the execution of all previously planned socially dangerous actions and the occurrence of the desired negative consequences.
Signs that the crime is over can be different:
- if the offense is material, then the moment of completion of the crime will be the time of the onset of the consequences of this offense (for example, a murder is considered completed after the death of the victim);
- if the corpus delicti is formal (that is, its essence does not include dangerous consequences), it will be recognized as completed from the moment the culprit commits the relevant actions (for example, robbery will be recognized as a completed crime from the moment the attack is committed, regardless of whether the criminal managed to take possession of someone else’s property or not );
- if the corpus delicti is alternative, then it will be completed at the moment of committing at least one of the actions included in the crime (for example, the production or sale of counterfeit securities or money will be recognized as a completed crime, even if the attacker simply printed the counterfeits and did not try to sell them At the moment).
Legal analysis of robbery, methods of its investigation
Legal analysis of robbery:
- The object is any property, valuable property, regardless of its form.
- Subject is a capable person over 14 years of age.
- The objective aspects of robbery include:
– evidence of the open nature of the crime;
– time frame and location of the robbery;
– seized property;
– aggravating circumstances and qualifying factors.
- The subjective side of the crime contains the presence of specific intent and desires for selfish purposes.
As soon as the criminal gains the opportunity to fully use and use the stolen property at his personal request, the crime is complete and complete.
Regarding the methodology for investigating robberies and robbery (due to the thin line between them), various types of investigative actions are carried out:
1. When detained on the spot:
- detention, search, examination of a suspect;
- identical actions in relation to the victim (instead of detention, an interrogation is carried out; instead of a search, an inspection is carried out);
- examination of the place where the crime was committed;
- questioning of witnesses;
- search of the suspect's place of residence;
- carrying out various examinations.
2. The criminal was not caught, but law enforcement officers have specific information about him (the opportunity to begin search activities with the subsequent detention of the culprit):
- interrogation, preliminary examination of the place, examination of the victim;
- inspection of the crime scene, interrogation of witnesses, examinations;
- search and detention of the culprit.
3. Absence of any information about the attacker:
- identical actions to those indicated above;
- identification of suspects;
- search activities to find stolen property;
- personal search of each of the suspects.
During the search, the main goals are to search and discover weapons, stolen property, and any other things that do not objectively belong to the suspect or were obtained during other robberies and robberies.
Arbitrage practice
Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court No. 29, dated 2002, “On judicial practice in cases of theft, robbery, robbery” provides explanations on the application of the law in terms of qualifying an act according to one or another composition. Based on the established practice of the courts, it is possible to resolve controversial situations when delimiting property crimes. Thus, the resolution establishes the following provisions:
- the crime will be considered completed when the offender can dispose of the property at his own discretion;
- robbery by a group of persons by prior conspiracy will also occur in the case when one person directly takes possession of the property, and the rest help him in this (open locks, break open doors, protect him from prying eyes, etc.);
- The participation in a crime of several persons, one of whom does not belong to the subject of the crime, is not a group of persons, i.e. under 14 years of age;
- home invasion occurs only when a criminal enters a home with the intention of stealing property. If the intent to steal arose after the penetration, i.e. was invited to visit, was with relatives, then the sign of penetration is not imputed.
Criminal sentence for robbery
According to Article 161 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, an attacker who is tried for robbery may face different types of liability. It depends on many factors, circumstances, severity of the crime, etc.
1. Robbery of someone else’s property in the “lightest” form is punishable by:
- community service (not exceeding 480 hours);
- compulsory work (no more than 2 years);
- restriction of freedom (2-4 years);
- forced labor (up to 4 years);
- arrest (up to 6 months);
- imprisonment (up to 4 years).
2. Robbery by a group of people under a criminal agreement, with unlawful entry, on a large scale, with the use of “light” violence:
- forced labor (not more than 5 years);
- imprisonment (up to 7 years) + fine up to 10 thousand rubles;
- restriction of freedom (up to 1 year or by court decision).
3. Robbery on an especially large scale by an organized criminal group:
- imprisonment (6-12 years) + fine 1 million rubles. (or equivalent income for 5 years);
- restriction of freedom (up to 2 years or by court decision).
Robbery is a dangerous crime due to its fine-grained nature. Too strong a blow - robbery. Got carried away with beatings - Article 105 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, murder. Law enforcement agencies and courts take robbery quite seriously, and it is almost impossible to get a suspended sentence - there is always an undisguised mercenary motive.
Get a lawyer's answer in 5 minutes
Responsibility
Criminal liability for robbery provides for various types of punishment depending on the crime committed and the presence of qualifying features.
When committing a crime qualified under Part 1 of Article 161 of the Criminal Code, the accused may be given the following punishment:
- compulsory or correctional labor;
- restriction of freedom;
- forced labor;
- arrest;
- deprivation of liberty.
According to Part 2 of Article 161 of the Criminal Code, the accused may be sentenced to punishment in the form of:
- forced labor;
- imprisonment with or without a fine, or with or without restriction of freedom.
Particularly qualified robbery (Part 3 of Article 161 of the Criminal Code) is punishable by imprisonment with or without a fine, or with or without restriction of freedom.
The terms and amounts of punishment vary. Only the court can determine the final punishment.
Home robbery
It is important to distinguish between residential robbery and residential theft. So, if a thief enters an apartment where the owners are absent, steals money and jewelry, and then calmly leaves, this is theft. If, having entered the house, the bandit sees the owners, but continues his criminal actions, it should be classified as robbery under Article 161 of the Criminal Code.
Bank robbery
As for a bank robbery, in the case when property is stolen by a group of masked robbers, the actions are classified as robbery or robbery (depending on the circumstances). Theft in a bank can only be carried out in the absence of people, for example, from a safe deposit box.
Note! A robbery has the characteristics of a robbery if it is committed with the use of threats of violence or their direct use. At the same time, the intent is always selfish - the theft of someone else's property with the aim of taking it. We will tell you more about the crime of robbery in this article https://lexconsult.online/8621-razboi-ponyatie-i-sostav-prestupleniya
Store robbery
A thief decided to steal a stick of sausage from a store. He knows very well that there are security and CCTV cameras here, i.e. realizes that he is being seen, but continues his actions anyway - this is robbery. The situation is also the same in the case when, at the moment when the thief was hiding the sausage, those around him noticed this and began to shout at him to stop his illegal actions. If the presence of cameras is not known, and the bandit is sure that he is acting secretly from everyone, it should be classified as theft.
Article 161 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation “Robbery”
According to statistics from the Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Russian Federation , robbery is one of the most common crimes of a selfish and violent nature.
Thus, in 2021 alone, more than 50 thousand cases of robbery were officially registered.
The increased social danger of robbery lies in the open method of theft, which the guilty person resorts to in order to take possession of someone else’s property, which distinguishes robbery from theft, as well as in the presence of harmful consequences for the personality of the victim and his rights: during robbery, harm to the health of citizens is possible, violation of inviolability is possible home, personality, freedom and other constitutional rights and freedoms.
It should be noted that robbery is one of the oldest crimes. From the earliest days of private property, individual members of society tried to take away property and other people. In order to prevent criminal attacks, laws were adopted punishing the commission of robberies.
In Russia, the first mentions of robbery as a separate crime date back to the 14th-15th centuries (Pskov Judgment Charter, Novgorod Loan Charter and other early Russian acts of rule-making). From the very first laws, robbery was viewed as an open form of theft, distinguished from robbery by the absence of violence dangerous to life and health.
Characteristics of the object of the crime
The object of such a crime is movable or immovable property, money and other valuables that a person wants to take possession of through criminal means.
Robbery is committed only in open form, but in some situations a criminal act of this kind can become secret. In particular, theft cannot be recognized as open in cases where the owner of the property or third parties do not see the actions of the criminal or consider their commission to be a lawful act.
Theft, which was initially planned as a secret crime, can become open. For example, if someone noticed the actions of a criminal, and the culprit, ignoring this fact, continues to realize his intentions.
A crime can be called completed, and the object of the crime - stolen, only in cases where the property has been confiscated. That is, after the guilty person has a real opportunity to use it, transfer it into the possession of third parties, and dispose of it for personal gain at his own discretion.
Statistics data
As of 2021, just under 5 thousand robberies were committed in the Russian Federation. Fortunately, approximately 70 percent of them were solved by law enforcement officers without delay.
However, there is also the remaining 30 percent in which the owners of the stolen property are unlucky and the identity of the robber cannot be determined.
Of course, in some cases, such crimes take years to be investigated, because the guilty person can only “prick up” in another robbery.
Do you need a lawyer?
Should I look for an experienced private lawyer or should I trust a public defender? Despite the fact that the sanction of Article 161 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation is an alternative one, you should not expect that the court will impose a punishment not related to imprisonment. As we have seen, the courts prefer to place citizens who have committed robbery in colonies. And the state lawyer has little motivation to ensure that his client does not receive a real prison sentence. Therefore, it is better to entrust the case to a qualified criminal lawyer.
Ideally, the lawyer seeks to conclude the criminal case (prosecution) as early as possible, before the preliminary investigation stage comes to an end. If this goal could not be achieved, the defender will strive to turn the situation in favor of his client further. So, it can achieve the following results:
- issuance of an acquittal;
- reclassification of the act to an article providing for a less severe punishment (for example, from robbery to theft);
- reclassification of the act to a part of the article providing for a less severe punishment (for example, from Part 3 to Part 1 of Article 161 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation);
- imposing the most lenient punishment without applying additional punishment provided for in the sanction of the article;
- assignment of a suspended sentence;
- assistance in parole.
If we are talking about victims of robbery, then the lawyer will help, firstly, to achieve the initiation of a case and bring the perpetrators to criminal responsibility, and secondly, will contribute to the recovery of fair monetary compensation from the convicted persons.
Contacting a lawyer at an early stage significantly increases the chances of a successful outcome of the case. However, you can also enlist the help of a specialist after the fact, when the verdict has already been passed: it is likely that the defense attorney will be able to find important “clues” and appeal the judicial act.
Robbery under Article 161 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation
Robbery, as well as theft, is a type of theft of property that belongs to another person by right of ownership. But unlike theft, robbery is characterized by an open method of implementation.
Accordingly, open robbery is considered an illegal act committed in the presence of strangers or the owner of the stolen property. At the same time, persons who observe the commission of illegal actions should be aware that these actions contradict current legislation and entail prosecution.
Such crimes have firmly taken a leading position among cases considered in court. However, the penalties applied for such illegal acts may vary. For example, criminal liability for robbery directly depends on the presence of aggravating or mitigating circumstances, accomplices in the crime or recidivism.