Noise from neighbors in an apartment building is not uncommon. Quietness and tranquility in an apartment building is rather rare. But it’s one thing when it’s household noise due to poor sound insulation in the building, and another thing when you systematically hear scandals, screams and sounds of beatings, and a child is involved in all this. What should neighbors do in such a situation?
You shouldn't ignore what's happening. In one of these scandals, something irreparable could happen. And this can be prevented if you promptly complain about the situation to regulatory authorities or call the police. We will tell you further what and how to do if your neighbors are constantly making noise and the child may suffer.
Where to go if neighbors beat a child?
It all depends on the specific situation.
If a child is severely beaten in your presence, call the police and wait for an order. Employees of the Ministry of Internal Affairs will record the fact of violence and take him to the hospital for examination. The forensic expert's report will show what injuries the child received and what type of liability the parents can be held liable for. The child will be temporarily isolated, and the perpetrators of the crime will have their parental rights limited. In the future, complete deprivation of rights to children is possible.
When you are just guessing about the beating, you should contact:
- to the local police officer - he will check and open a criminal case;
- to the guardianship and trusteeship authorities - they will conduct an inspection, if necessary, involve the police and file a claim for deprivation of parental rights;
- to the prosecutor's office - he will deal with the situation in a dysfunctional family, and also monitor the work of the police and guardianship authorities;
- to the Ombudsman for Children's Rights - get acquainted with the situation in the family, send requests and requests for verification to the police, guardianship or prosecutor's office (the longest route).
Some turn to the media for help. However, it must be understood that this is an open judgment. At the same time, a public defender can become a victim of criminal prosecution.
If you see parents beating a child, call the police. If you suspect domestic violence, contact guardianship.
What signs indicate domestic violence?
Checking a dysfunctional family will be required if:
- in the neighboring apartment there is often shouting and children’s crying is heard;
- the child looks exhausted, fearful, with bruises and abrasions;
- the mother or father avoids talking about the psychological and physical state of their child;
- friends or classmates say that he is being beaten;
- Other neighbors gossip about abusive parents.
Domestic violence is often hidden, but it can be identified.
From scratch
“He asked for forgiveness, and I returned,” is how 70 percent of women who visited the center ultimately answer. Its director Natalya Zavyalova explains that it is difficult for them to overcome themselves and decide on a new life: “We find out what a woman wants: get a divorce, move or find a job. There were cases when we helped with professional retraining. But if a person does not want to change, no one will force him to do so.”
But thirty percent decide to make changes! That is, every third! According to Zavyalova, every year Muscovites become more self-sufficient and less and less afraid to talk about domestic violence. Every day more than 100 people contact the center with various questions. During the year - about 15 thousand Muscovites, including men.
Good to know
What should a teenager who is beaten at home do?
A child who is being abused at home should first look to his community for help. For example, at school. It is enough to turn to a teacher who inspires trust. The teacher will independently notify the guardianship authorities. Employees will check and notify the police.
You can share with friends. They will tell their parents or relatives who are ready to help the child in a difficult situation. If there are no people who would like to open up, you can go to the emergency room with signs of beatings. It is not necessary to tell what happened - the doctors themselves will report the injuries to the police, who will find out everything.
Many teenagers are afraid to tell others about their torment in the family, experiencing constant pain and humiliation. There is no need to hide your fear and physical injuries. There are many caring people around who are ready to help: teachers, acquaintances, neighbors. They will contact law enforcement agencies, who will provide you with assistance and protection. You can also call special hotline numbers and tell about your problem.
The unified all-Russian helpline for children, adolescents and their parents is 88002000122.
Do not be silent
The crisis center for helping women and children is located on Dubki Street, 9a.
Mothers and their children can stay here for a week or even two months, depending on the situation. Doctors and psychologists will help you come to your senses after a family drama. Here you can get legal advice and process lost documents. …27-year-old Larisa, a single mother of five children, came here at the beginning of summer. The woman told a chilling story about how she was physically assaulted almost every day by her partner Andrei. Patience ran out when he began to threaten the lives and health of children. The man was in no hurry to acknowledge paternity; he also did not bother to register in the capital. He didn’t spoil his family with money and didn’t bother himself with constant work. But family income, which consisted only of social payments and benefits, was disposed of right and left. As a result, Larisa did not always have enough money even for food for the children.
Crisis Center specialists are not surprised by such stories. They immediately set about restoring order. We drew up a plan to work with the family to overcome the crisis. The woman and children were placed in a cozy room with modern furniture and a bathroom, where they finally felt completely safe. The family ate in the dining room. The children spent the day studying in the playroom and meeting with psychologists. Along with the rehabilitation course, the family also received social and legal assistance. Andrei's paternity was established in court. Alimony was collected from him.
The center is now also helping 51-year-old Muscovite Irina, who came with her 15-year-old daughter Olga. The girl’s father did not touch his wife, but he “raised” the child from the heart. After another quarrel, which ended with a concussion and numerous bruises to the teenager’s face and body, Irina and Olga ended up in the emergency room. Then we decided not to return home, but to go to the center. After conversations with Irina, experts found out that her husband had always been cruel to children. Initially, he used force on his son until he left to study in another city, and then switched to his daughter. The atmosphere in the family became tense, especially since the teenage girl did not remain silent and told her father about inappropriate behavior. Why was the mother silent? I couldn’t stand up to my husband for fear of angering him even more. So she lived for many years with a bitter feeling of guilt in front of her children.
The mother and daughter were left at the center for four months. We drew up a rehabilitation plan, as well as a long-term action plan for all family members for the year. After individual sessions with a psychologist and art therapy with other children, the girl’s emotional state stabilized. She began to sleep normally and eat with appetite. Enjoys participating in the social life of the school. Successfully passed the state final certification. And in order to see less of her father, she went to study at one of the colleges in St. Petersburg. Irina works in Moscow, rents a room from a friend for a nominal fee and plans to exchange the apartment she shares with her husband - the center is helping her with this.
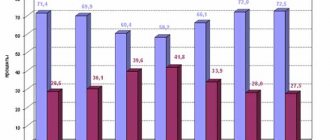
Infographics "RG" / Alexander Chistov / Angelina Zhukova
Article for child abuse
For child abuse, the perpetrators face inevitable punishment. If a teenager has been repeatedly subjected to beatings that did not cause harm to health, the perpetrator faces punishment under Art. 6.1.1 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation:
- fine from 5 thousand to 30 thousand rubles;
- arrest up to 15 days;
- compulsory work from 60 to 120 hours.
If the parent has already been prosecuted under an administrative article, a repeated violation will already face criminal liability under Art. 116.1 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation. He will face tougher sanctions: the fine will increase to 40 thousand rubles, compulsory work - up to 200 hours, arrest - up to three months. Another preventive measure is being introduced - correctional labor for up to six months.
For domestic violence, people are first brought to administrative and then criminal liability.
The matter takes a different turn if the child is harmed. A negligent parent will immediately be charged with a criminal offense:
- for minor harm - under Art. 115 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation;
- for harm of moderate severity - under Art. 112 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation;
- for grievous harm - under Art. 111 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
The extent of damage caused is determined by forensic medical examination. The perpetrator faces not only a criminal record, but also a real prison sentence of up to 15 years.
Another way of bullying children, for which you can end up in the dock, is torture. Sanctions are established by Art. 117 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation. For intentionally inflicting physical or mental suffering on a minor through systematic beatings or violent acts, the person faces imprisonment from 3 to 7 years.
Parents will also be punished for cruel treatment under Art. 156 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation:
- fine up to 100 thousand rubles. or in the amount of the perpetrator’s income for a period of up to a year;
- compulsory work up to 440 hours;
- correctional labor for up to two years;
- forced labor or imprisonment for up to three years.
Anyone guilty of beating a child can be sent to prison for a long time.
Guardianship complaint against parents
As a rule, in order to contact an institution it is necessary to file a complaint with all the necessary details. The laws state that parents, as well as guardians who have taken into their family for upbringing, must properly fulfill the responsibilities for raising and maintaining children. A complaint against the authorities may be made if signs of beatings are found in kindergartens or other institutions. When drawing up documents, you must follow all the rules of drafting that apply to an official document. A document that is drawn up in an improper form may not be accepted by the guardianship authorities and may be sent for correction. And this may take additional time.
Summarize
When a child is beaten in the family, it shows. Traces of beatings cannot be hidden. And there are caring people who are ready to help a child who has suffered from violence. They turn to various structures that can legally protect the child and punish abusive parents. Assault and abuse of a defenseless child is a crime, so the punishment for beating children is severe. However, not only strangers, but also the child himself can hold parents accountable by talking about his problem. For this purpose, there are helplines and various centers if a teenager is afraid to contact law enforcement agencies.
“Take it on your phone and call the police.” How to react if someone else's child is beaten in front of you
“Having returned from school, my son said that he noticed a classmate had many bruises on his arms and legs. Should I report this somewhere?” – the mother wondered on Facebook. TUT.BY asked experts to explain how to act correctly in such situations in order to help the child without harming them.
The photograph is used as an illustration. Photo: BBC
Our interlocutors:
Andrey Solodovnikov , board member of the international public organization "Understanding". From 2003 to 2011, Secretary of the Commission on Minors' Affairs under the Council of Ministers
Mikhail Gotovchits , head of the department for supervision over the implementation of legislation on minors and youth of the Minsk City Prosecutor's Office
Evgeniy Abramovich , deputy head of the prevention department of the Department of Public Safety and Internal Affairs of the Central Internal Affairs Directorate of the Minsk City Executive Committee
Legislative regulation
- International regulations;
- Hague Convention 1961;
- Minsk Convention 1993;
- Constitution of the Russian Federation, art. 7, art. 38;
- Civil Code of the Russian Federation Art. 34;
- Family Code of the Russian Federation;
- Criminal Code of the Russian Federation Art. 156;
- Federal Law of April 24, 2008 N 48-FZ “On Guardianship and Trusteeship”, Art. 7, 8.24;
- Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of November 17, 2010 N 927 “On certain issues of guardianship and trusteeship in relation to adult incompetent or partially incompetent citizens”