- What cases are tried by jury?
- Grounds for consideration of a criminal case by a jury
- Number of jurors
- Selection of juror candidates in Russia
- Who cannot be a juror in Russia
- Who may be excluded from the list of juror candidates?
- Material support for jurors
- Powers of jurors
- Other features of jury trials in Russia
Jury trials first appeared in Russia in 1864. After being abolished in 1917, jury trials as a form of administration of justice were reintroduced in Russia in 1993, initially as an experiment in five regions of the country, then in 2004, jury trials began to operate in all regions except Chechnya, and only from 1 In January 2010, this institute finally began to operate throughout the Russian Federation.
So, according to Part 2 of Article 47 of the Constitution of the Russian Federation, everyone accused of committing a crime has the right to petition for a trial of his case with the participation of a jury in cases where this is permitted by law.
The consideration of criminal cases with the participation of jurors is regulated by the Federal Law “On jurors of federal courts of general jurisdiction in the Russian Federation” No. 113-FZ of August 20, 2004, and the procedural procedure for the participation of jurors in the consideration of criminal cases by courts is regulated by Chapter 42 of the Criminal Procedure Code RF.
Assistance from a lawyer on legal issues. Tel.+7 Telephone consultation
What cases are tried by jury?
According to Russian legislation, the participation of jurors is provided only in criminal proceedings.
But not all criminal cases are tried by a jury.
The categories of criminal cases subject to trial with the participation of jurors are limited to the list specified in paragraphs 2 and 2.1 of part two of Article 30 of the Criminal Procedure Code of the Russian Federation, these include:
- criminal cases involving crimes punishable by life imprisonment or death penalty
- criminal cases of other especially serious crimes within the jurisdiction of the regional (territorial) court
Below is an exhaustive list of criminal cases that can be tried with the participation of jurors, divided into groups:
1.The first group includes crimes directed against inalienable fundamental constitutional human rights - the right to life and freedom, regardless of official, social or national status:
- Murder (Article 105 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation)
- Intentional infliction of grievous bodily harm, resulting in the death of the victim through negligence (Part 4 of Article 111 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation)
- Kidnapping (Part 3 of Article 126 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation)
- Attempt on the life of special victims (Articles 277, 295, 317 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation)
2.The second group includes crimes against public safety:
- Banditry (Article 209 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation)
- Organization of a criminal community committed by a person who occupies a high position in the criminal hierarchy (Part 4 of Article 210 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation)
- Theft of air, water, railway transport (parts 1–3 of Article 211 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation)
- Piracy (Article 227 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation)
3.The third group includes crimes against the peace and security of mankind:
- Aggressive war or calls for it (Articles 353, 354 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation)
- Rehabilitation of Nazism (Article 354.1 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation)
- Development, production, stockpiling, acquisition or sale of weapons of mass destruction (Article 355 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation)
- Violation of the rules of warfare (Article 356 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation)
- Genocide (Article 357 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation).
- Ecocide (Article 358 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation)
- Simple and qualified mercenary offenses (parts 1 and 2 of Article 359 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation)
- Assault on persons under international protection (Article 360 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation).
4. The list is completed by the fourth group of crimes directed against public health and public morality:
- Drug smuggling (Part 4 of Article 229.1 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation)
- Illegal drug trafficking (Part 5 of Article 228.1 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation)
Official website of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation
Amendments regarding the institution of jurors come into force on June 1
MOSCOW, June 1.
/TASS/. The jury in Russia has significantly expanded its competence since June 1 - the law on amendments to the Code of Criminal Procedure, initiated by the President of Russia, has come into force. It includes three main innovations - the possibility of trying cases with a jury in district and garrison military courts, the possibility of trying cases by jury against women, as well as men over 65 years of age (previously they did not have the right to a jury trial, since they cannot be the most severe form of punishment was applied - life imprisonment), and also expands the number of articles of the Criminal Code, cases under which a jury can consider.
Jury trial in district courts
In connection with the extension of jury trials to district and garrison courts, criminal cases under Part 1 of Art. 105 (murder without aggravating circumstances) and part 4 of Art. 111 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation (intentional infliction of grievous bodily harm resulting in the death of the victim).
In addition, as explained to TASS in the Supreme Court, the jurisdiction of the jury court in criminal cases for crimes under Part 2 of Art. 105 (murder with aggravating circumstances), part 5 of Art. 228.1 (illegal production, sale or transfer of narcotic drugs on an especially large scale), Part 4 of Art. 229.1 (smuggling of drugs by an organized group, either on a particularly large scale, or with the use of violence against a person exercising customs or border control), Art. 277 (attack on the life of a state or public figure), Art. 295 (attack on the life of a person administering justice or preliminary investigation), Art. 317 (attack on the life of a law enforcement officer) and Art. 357 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation (genocide), which were previously excluded from the jurisdiction of the jury in cases where life imprisonment could not be imposed on the defendants as the most severe type of punishment.
These criminal cases will be tried by a court consisting of a district or garrison military court judge and a panel of six jurors (and two reserves).
The jurisdiction of criminal cases by the jury at the level of regional and equal courts (where the current 19 articles of the Criminal Code for the most serious crimes, for which life imprisonment or the death penalty is provided, remains within the jurisdiction of the jury), additionally includes cases under the same articles in relation to older women 18 years old and men over 65 years old. But the composition of this court will change - it will consist of a judge from a regional or equivalent court and a panel of eight jurors (previously - 12 jurors).
Thus, only criminal cases involving crimes committed by persons under the age of 18 remain outside the jurisdiction of the jury.
Jury reform
Over the past decade, the competence of the jury in Russia has been declining. At the end of 2008, cases under nine elements of the Criminal Code were excluded from it - terrorist attack, hostage-taking, organization of an illegal armed group, mass riots, treason, espionage, violent seizure of power, armed rebellion, sabotage; at the end of 2010 - criminal cases containing information on state secrets, and criminal cases against members of the Federation Council, State Duma deputies and judges.
Later, after the transfer of 20 crimes, including cases of bribery, crimes against justice (contempt of court, illegal prosecution or exemption from criminal liability), crimes against sexual freedom and sexual integrity, from regional courts to district ones, they also left the jurisdiction of the jury . As a result, if before 2010 jury courts considered more than 500 criminal cases per year, then in the last three years - just over 200 cases annually.
In December 2015, Vladimir Putin supported the proposal, voiced during a meeting with human rights commissioners and members of the Human Rights Council, to expand the role of the jury and initiated a bill of amendments to the Code of Criminal Procedure.
Scope of reform
According to experts, the number of cases tried with the participation of a jury may increase 70 times - up to 15 thousand per year. First of all, due to the inclusion of jury cases under Part 1 of Art. 105 (murder without aggravating circumstances) and part 4 of Art. 111 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation (intentional infliction of grievous bodily harm resulting in the death of the victim). Annually under Part 1 of Art. 105 sentences are passed against 6–7 thousand defendants under Part 4 of Art. 111 - in relation to 5-6 thousand. Now they have the right to petition for their cases to be considered by jury courts.
To exercise the right to a jury trial, 2.3 thousand halls were equipped in district and garrison courts, including deliberation rooms and video surveillance on the way to them in order to protect jurors from possible influence from other participants in the process. Almost 7 thousand judges and almost 9 thousand court staff were trained for the new form of work; the Prosecutor General's Office organized educational seminars for public prosecutors in all federal districts.
Right to trial by jury
As explained to TASS in the Supreme Court of Russia, “the possibility of filing a petition for a trial by jury by persons accused of committing crimes, criminal cases for which from June 1, 2018 will become subject to the jurisdiction of this court, will depend on the stage at which this court will be moment of proceedings. Before the court appoints a criminal case for consideration, the accused will have the right to file such a petition.” The Code of Criminal Procedure of the Russian Federation provides for the possibility of appeal and cassation appeals against decisions made by a court with the participation of a jury, with certain restrictions established by law.
Given the shortening of the jury pool, a guilty verdict in a district court (with a panel of six jurors) requires at least three votes from the jury to vote for the defendant's guilt.
In recent years, jury trials have shown that they are more likely to acquit than in ordinary cases. In 2021, out of 318 thousand defendants whose cases were considered by the court in a general manner, 67% (212 thousand) were convicted, 0.9% (2.9 thousand) were acquitted, 1.2% (3.9 thousand) cases were terminated on rehabilitating grounds, in relation to 28% (90 thousand) - on non-rehabilitating grounds. 11% (23 thousand) courts commuted the charges. Taking into account cases considered in a special order, in 2017, 0.3% of defendants were acquitted.
Following jury verdicts in 2021, 446 people were convicted and 52 (10%) were acquitted.
Over the past 10 years (2008–2017), jury trials have considered 4,139 criminal cases. According to their verdicts, 7,680 people (83%) were convicted, 1,544 (16%) were acquitted.
Jury candidates
To create lists of jury candidates for 2021, subventions in the amount of 517 million rubles were allocated from the budget to the regions. As TASS was told in the judicial department at the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation, the required number of jury candidates for work in regional and district courts is presented to regional authorities by the chairmen of the highest regional courts. If the population in municipal areas is insufficient, regions have the right to create a judicial district from several municipalities with a single list of candidates for several courts.
According to the Judicial Department, according to information received from the regions, 5 million 937.6 thousand people will be included in the lists of jury candidates in 2021. 16 regions asked for additional funding to compile the lists. As the Supreme Court previously explained, to form a jury in a regional court, at least 14 candidates must be summoned to appear in court, and in a district and garrison court - at least 12 candidates.
Jury pay
The jurors can be citizens permanently residing in the area, over the age of 25, who do not have an outstanding criminal record, who have not been declared incompetent, and who are not registered with a drug treatment or psychoneurological dispensary. Suspects or accused of committing crimes who do not speak the language in which the proceedings are conducted, or who have physical or mental disabilities that prevent full participation in the consideration of the case are not allowed to serve as jurors. A citizen has the right to refuse to serve on a jury if he is over 65 years of age, either for health reasons, or if he is a civil servant, military personnel or clergyman. Within five years after dismissal from service, judges, prosecutors, investigators, investigators, lawyers, notaries, bailiffs, private detectives, employees of the FSB, FSO, SVR, Ministry of Internal Affairs, FSIN and customs may refuse to serve as jurors. Candidates for jury service may be summoned to appear in court once a year.
During the time a juror performs his duties, the court pays him a compensation in the amount of half the official salary of a judge of this court in proportion to the number of days the juror participates in the administration of justice, but not less than the average earnings of the juror at the place of his main work. In addition, the juror is reimbursed for travel to and from court and hotel accommodations.
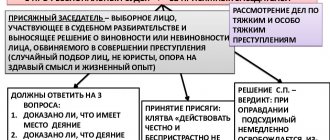
Grounds for consideration of a criminal case by a jury
Jurors are invited to participate in a criminal case solely at the request of the accused. The court cannot arbitrarily, at its own discretion, involve jurors in the consideration of a case.
A request to consider the case by a court with the participation of a jury may be submitted by the accused after familiarization with the case materials during the preliminary investigation (Part 5 of Article 217 of the Code of Criminal Procedure of the Russian Federation) and before the appointment of a court hearing (Clause 1 of Part 5 of Article 231 of the Code of Criminal Procedure of the Russian Federation). Please note that we are talking about scheduling a trial on the merits of the case, i.e. the judge makes a corresponding decision, which determines the composition of the court in a criminal case.
The defendant’s request to have the case examined by a court with the participation of a jury is considered in a closed court session in the manner of a preliminary hearing in a criminal case (Part 1 of Article 234 of the Code of Criminal Procedure of the Russian Federation).
But not all categories of defendants have the right to trial by jury. The exception is criminal cases of crimes committed by persons under the age of 18, even if they have been charged with the above-mentioned crimes.
Such cases remain beyond the jurisdiction of a jury.
In other cases, the accused cannot be denied a trial by jury, provided that the norm under which he is charged is included in the list of acts where a jury trial is permissible.
A little history
Trial by jury originated in medieval England. In modern times, the English authorities tried to limit this judicial institution, but the people's legal consciousness was on its side, so by the 19th century it was finally institutionalized. The defendant received the right to an obligatory defense lawyer; it was forbidden to mistreat the defendant.
In the 19th century, trial by jury on the English model was introduced in France, Germany, Austria-Hungary, Italy, Spain and Norway. Russia was no exception. One of the most successful of the Great Reforms of Alexander II was the judicial one (1864). The jury in Russia tried three times more cases than in France, and four times more than in Austria. The jury trial of that era is described in detail in classical Russian literature, in particular in the novel by F.M. Dostoevsky "The Brothers Karamazov".
One of the first steps of the Bolshevik government was to abolish jury trials in 1917. It was restored in Russia only in 1993. In 2008–2013 The powers of the jury were significantly reduced.
In Russia, juries decide only factual questions: whether a crime was committed or not, whether the defendant committed the crime, whether the defendant is guilty of committing it, whether he deserves leniency. Issues of law, for example, the legal qualification of the crime, the imposition of punishment, the resolution of a civil claim, remain with a professional judge.
Today in Russia the share of acquittals in general is about 1%, and when a case is tried by a jury it is 15–20%. However, courts often overturn acquittals by juries “due to significant procedural violations.”
Selection of juror candidates in Russia
There is a clearly regulated procedure for selecting jurors.
First of all, these are the requirements for jurors; below we will dwell on this in more detail.
The panel of jurors is formed at a separate stage of the legal proceedings, candidates are selected from those people who were called for selection to the court.
People are called from a special list that has been valid for 4 years and prepared by the executive body of state power of the subject. This list is prepared on the basis of current information about the population in the region (krai), through random sampling.
Information about the number of people is taken from the same sources that are used before the elections (State Automated System “Elections”).
The generated lists are sent to the court, where the selection of jurors who will directly participate in the consideration of the case takes place. The selection is carried out according to the criteria provided for by Federal Law No. 113-FZ.
Procedure and time for creating a register of candidates
According to Article 5 of Federal Law No. 113, for a period of at least 3 months. Before the completion of the terms of office of candidates for the collegium of assessors, chairmen of judicial bodies must submit updated lists.
Such authorities include:
- Russian Armed Forces;
- regional organs;
- regional municipalities;
- departments of federal cities;
- autonomous region and districts.
Potential jurors are determined by software in a random order using an automatic method through the GAS “Elections” system, the creation of which was decided by the President in 1994 according to Decree No. 1723.
This register contains personal information of individuals participating in election campaigns and referendums. Exclusion from jury lists in the courts of the Russian Federation is carried out on the basis of Art. No. 3 part No. 2 of the current law.
The procedure for approval of the list of board members by the executive department for the region of the Russian Federation:
- Sending notifications to citizens registered in the territory of the subject of the location of the court.
- Within fourteen calendar days, people on the register must familiarize themselves with the invitation.
- Consideration of applications received from potential applicants.
- Checking applicants for compliance with selection criteria.
- Making adjustments and eliminating inaccurate data about citizens included in the general jury register.
- Drawing up and approving the list of board members.
Who cannot be a juror in Russia
The list of persons whose participation in a criminal case as a juror is excluded is given in Article 3 of the Law of the Russian Federation “On jurors of federal courts of general jurisdiction in the Russian Federation”, these include:
- Persons who, at the time of compiling the relevant lists of candidates, have not reached 25 years of age
- Persons whose criminal record has not been expunged or expunged
- Incapacitated or partially capable persons (this is confirmed by a court decision that has entered into legal force)
- Persons suffering from alcoholism, drug addiction, substance abuse, chronic mental disorders and, in this regard, registered with a narcologist or psychiatrist (PND, ND).
- Persons suspected or accused of committing crimes
- Persons who do not speak the language in which legal proceedings are conducted (for the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation, the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation, cassation, appeal, arbitration and military courts this is Russian; for other courts of general jurisdiction - Russian or the state language of the corresponding republic)
- Persons who, due to mental or physical disabilities, are deprived of the opportunity to take full part in the judicial process
The specified list is closed and cannot be expanded arbitrarily, i.e. in the absence of the above circumstances, any citizen may be included in the preliminary list of juror candidates.
If any of the above circumstances becomes clear after a citizen has been included in the preliminary lists of juror candidates, then after such circumstances are clarified, he is subject to mandatory exclusion from such lists.
Jury rights under the law
To assume their rights, jurors take an oath, and only after that the trial of the case begins. During the trial, jurors may:
- communicate with the persons being interrogated, but not directly, but through the presiding officer;
- examine the circumstances directly related to the case and the evidence involved in it, but only the evidence that has been designated as admissible is examined; the very question of the admissibility of evidence is decided by a judge without a jury ;
- ask for clarification of legislative norms and legal terms used by other participants in the process;
- keep your records and use them in the future.
for jurors : they cannot leave the courtroom during the hearing, communicate with persons not related to the court, collect information about the case on their own, and disclose the secrecy of voting.
Taking into account the powers of jurors , we can say that the trial is organized so that they make a decision based on the information presented for consideration. But what information is presented to them is decided by the judge.
Who may be excluded from the list of juror candidates?
After the lists of candidates, including reserve ones, have been formed, exclusion from them is made based on written statements of candidates for jurors, in the following cases:
1.It was revealed that the citizen does not meet the requirements established by law for a juror, that is, those requirements listed in Article 3 of the Federal Law “On jurors in federal courts of general jurisdiction of the Russian Federation” (this is the basis for the mandatory exclusion of a candidate from the lists)
2.The candidate for juror reported in writing the reasons why he cannot serve as a juror, namely:
- does not speak the language of the proceedings in which the process is conducted
- is unable to perform the relevant duties due to health reasons (this must be documented)
- reached the age of 65 years
- holds a public or elected position in local government
- is a military serviceman
- Five years have not passed since the date of his dismissal from military service under a contract from the FSB, state security or foreign intelligence agencies
- is a judge, prosecutor, lawyer, investigator, investigator, notary, private detective, bailiff, or ceased to hold the corresponding position less than five years ago
- is an employee of the Department of Internal Affairs, the Federal Penitentiary Service, customs authorities with a special rank, or was dismissed from the relevant service less than five years ago
- is a clergyman
Also, a candidate for jury may be excused from participating in the case if he declares that he has other valid reasons, which include the following:
- the candidate for juror is over 60 years old
- female juror candidate has children under 3 years of age
- a candidate for juror, due to his religious beliefs, does not consider it possible for himself to participate in the administration of justice
- the position (profession) held by a candidate for jury does not allow him to be distracted from his professional and official duties without significant damage to public and state interests (doctors, airline pilots, teachers, etc.)
This list of reasons is not final, which means that each candidate for jury can declare other, purely individual reasons that do not allow him to participate in the criminal process.
So, if there are good reasons, the candidate for jury will be excluded from the preliminary lists and released from further participation in the selection, having previously explained to him that, if he wishes, he can still take part in the process.
How the jury list has been shortened
In 2021, Federal Law No. 190 came into force, on the basis of which a number of provisions in various legal acts have undergone changes. The updates are presented in the form of a set of measures aimed at achieving a compromise between the interests of the state and the public. One of the types of amendments adopted on 01/01/18 was the number of jurors in court.
The change in the composition of candidates for assessors consists of reducing them. District authorities and garrison authorities require the participation of 6 people. To form a board in 2020, 12 representatives from the people are enough. Only 8 citizens will be called up to a higher department if there are at least 14 candidates.
Previously, before the 2021 reform, in the process of considering a criminal case, there were 12 members of the board, which were formed from 20 applicants.
Material support for jurors
During the performance of his duties in the administration of justice, the relevant court pays a juror, at the expense of the federal budget, a compensation in the amount of half the official salary of a judge of this court in proportion to the number of days of participation of the juror in the administration of justice, but not less than the average earnings of the juror at the place of his main work for such a period.
The juror is reimbursed for travel and transportation expenses in the amount established for judges of this court.
The time a juror performs his duties in the administration of justice is counted towards his length of service.
How long does the trial last?
The law provides for the involvement of citizens as jurors for 10 days. But if the trial of the case requires more time, then their term of service as a jury is extended. In special cases, cases can drag on for several months.
Have a question for a lawyer? Ask now, call and get a free consultation from leading lawyers in your city. We will answer your questions quickly and try to help with your specific case.
Telephone in Moscow and the Moscow region: +7
Phone in St. Petersburg and Leningrad region: +7
Free hotline throughout Russia: 8 (800) 301-39-20
Other features of jury trials in Russia
- A criminal case in which several defendants are involved is considered by a court with the participation of a jury in relation to all defendants, if at least one of them submits a petition for consideration of the criminal case by a court of this composition. However, if one or more accused are against consideration of the case by a jury, the investigator, if possible, separates the criminal cases against such accused into separate proceedings. In the absence of such a procedural possibility, the criminal case will be tried with the participation of a jury, regardless of the consent of all the accused.
- If the accused is charged with several elements of a crime, of which only one element is within the jurisdiction of a jury, then when the accused submits a petition for trial by a jury, the entire criminal case will be considered by a jury, despite the fact that not all elements of the crime are within the jurisdiction of a jury.
- The judge's decision to consider a criminal case by jury is final. This means that the defendant’s subsequent refusal to consider the criminal case by a jury will not be accepted.
- If several persons are accused in a case that can be tried by a jury, all of them must be provided with defense lawyers, regardless of what articles of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation they are charged under.
- During the consideration of the case, jurors are subject to guarantees of independence and immunity of judges established by law.
- A candidate for jury cannot be held liable for failure to appear in court, since such liability is not provided for by law for a candidate. In accordance with Art. 327 of the Code of Criminal Procedure of the Russian Federation, a candidate for juror receives the status of a juror after he is included in the list of jurors during the preparatory part of the court session from among the candidates who arrived in the courtroom, and only from that moment does he bear the statutory responsibility for failure to fulfill the duty of a juror.
- By virtue of Part 3 of Art. 333 of the Code of Criminal Procedure of the Russian Federation for failure to appear in court without a good reason, a juror may be subject to a monetary penalty.
High-profile cases
In the 1870s, juries often acquitted those who fought the tsarist regime. The most notorious was the case of Vera Zasulich. This populist terrorist shot at St. Petersburg mayor F. F. Trepov, who ordered her husband, populist A. S. Bogolyubov, to be flogged.
Instead of a sentence of 20 years of hard labor, the jury completely acquitted Zasulich. After this, in 1878, 1882, 1885 and 1889, laws were passed to remove a number of crimes from the jurisdiction of the jury.
In 1885, in the Vladimir district court, the jury acquitted 33 striking workers of the Morozov factory. The assessors pointed out the difficult situation of the workers and violations by the administration of the manufactory.
In the new Russia, the first jury trial took place in December 1993 in the Saratov Regional Court over the brothers Arthur and Alexander Martynov. They were accused of deliberately killing three people for mercenary reasons with particular cruelty. By decision of the jury, the brothers’ act was reclassified to a much milder article of the Criminal Code, which gave them a shorter prison term.
You can write a lot and interesting things about jury trials. But I won't take up your precious time. So I don’t say goodbye, your Gennadievna.
Formation of the board
Before the jury selection begins, the presiding judge introduces the candidates to the parties to the trial, tells them the essence of the case under consideration, and explains to them the tasks and conditions for participation in the administration of justice. Any participant in the process has the right to ask questions, including personal ones, to candidates that may help identify circumstances that impede a fair process. Based on the responses received, any number of candidates can be excluded from the lists by submitting reasoned challenges.
Moreover, each of the parties to the process has the right to unmotivated challenge of candidates, that is, to exclude them without indicating any grounds.
Other participants in the process
The consideration of the case with the participation of jurors occurs with the mandatory participation of:
- state prosecutor (prosecutor) supporting the prosecution in court on behalf of the state;
- a lawyer (defender) who protects the rights and freedoms of the defendant;
- victim (victim of a crime);
- defendant (accused of committing a crime).
If a person works, how can he leave work for so long?
The law requires an employer to release an employee selected for jury duty. Moreover, he does not have the right to deprive this employee of benefits or transfer him to another position, much less fire him.
If there is no one to replace the employee, his manager has the right to file a petition to relieve the employee from serving as a jury. But the satisfaction of this request is the prerogative of the court.