Everyone understands in general terms what a “criminal record” is. In legal terms, a criminal record is a specific legal consequence of convicting a person on behalf of the state for a crime. But what does a “expunged” or “expunged” criminal record mean, and what legal consequences does it have for a citizen? AiF.ru spoke with lawyer Vladimir Kuleshov about this .
Question and answer Can a borrower with an expunged criminal record take out a loan?
What is an expunged criminal record, and what is an expunged one?
Vladimir Kuleshov draws attention to Article 86 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, according to which a person convicted of committing a crime is considered to have a criminal record from the day the sentence enters into legal force until the criminal record is expunged or removed. Expungement of a criminal record is, in essence, the automatic termination of such status at the end of the period established by law. In addition, a criminal record can be expunged early, i.e. before the expiration of the repayment period provided for by the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, if the convicted person, after serving his sentence, behaved impeccably, compensated for the damage caused by the crime, and applied to the court with a petition to have his criminal record removed. “It should be noted that a criminal record can also be cleared by an act of amnesty or pardon,” says the expert.
Vladimir Kuleshov emphasizes that a person with a criminal record, during its term, is limited in the choice of profession and place of work (study), for example, he cannot study in some educational institutions, work in sensitive organizations, serve in law enforcement agencies, etc. Persons those with a criminal record do not have the right to purchase, store or carry civilian weapons. They have restrictions in the field of voting rights, in choosing a place of residence, etc.
The criminal legal consequences of having a criminal record are that it is taken into account when determining recidivism of crimes and when assigning punishment. In turn, the presence of a relapse is a circumstance that aggravates the punishment (clause “a”, part 1, article 63 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation). Punishment for recidivism is imposed in a more strict manner (Article 68 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation). The presence of a criminal record also influences the assignment of a prison sentence to a type of correctional institution (Article 58 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation). In addition, it limits or completely excludes the possibility of applying to a person who has committed a crime again, exemption from criminal liability and punishment (Articles 75, 76 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation), the expert lists.
Question answer
Can a company refuse to hire a candidate because of an expunged criminal record?
What are the features of expunging and expunging a criminal record?
When a criminal record is expunged after the expiration of the period established by the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, the legal consequences of the criminal punishment imposed by the court are automatically and unconditionally annulled. The period for expunging a criminal record depends on the category of severity of the crimes committed by the person, as well as on the age at which they were committed.
The second option is early expungement of a criminal record through the court, which is carried out at the request of a person who has served his sentence. The basis for the court's decision is the positive characterization of the convicted person, presented by the criminal-executive inspection of the Federal Penitentiary Service of Russia, and other documents indicating that the person behaved impeccably and also compensated for the harm caused by the crime.
Separately, provided for in Articles 84 and 85 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, the possibility of early expungement of a criminal record by an act of amnesty issued by the State Duma of the Russian Federation or by the Decree of the President of the Russian Federation on the pardon of a specific person.
The employer chooses a person with a clean certificate
Meanwhile, after the introduction of a new form of certificates into practice, many citizens lost the opportunity to freely find employment in vacant jobs, and some even lost their jobs. Because these certificates began to display information about long-expunged or expunged convictions for crimes that were committed in the distant past, sometimes even several decades ago. The situation was aggravated by the fact that employers began to demand such certificates from almost everyone, including current employees, even in cases where they did not have the right to it.
For several years now, these new police clearance certificates have caused a storm of indignation from the public. And most recently, this position was supported by the Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Republic of Kazakhstan, together with the Prosecutor General’s Office of the Republic of Kazakhstan, approving the proposal of the regional director of the non-governmental organization “Penal Reform International” in Central Asia, Azamat Shambilov, on the complete abolition of police clearance certificates in their current form .
Let's now imagine the following situation: the employer requested such a certificate from a current employee who once had problems with criminal law, the employee brought it... And let it indicate at least three times that his criminal record has been expunged or removed, or that the person has not been prosecuted at all in connection with release from court on one or another non-rehabilitative grounds, such a person will most likely be dismissed. Just in case.
What will happen if the workforce is reduced and the employer begins to choose who to fire? Moreover, this particular employee will be fired, with a “stained” certificate. Yes, it will be illegal, but not everyone will find enough persistence and strength to sue the owner or defend their rights in another way. Indeed, in this case, the employer will still, in the end, find a way to fire the unwanted employee for some other reason.
Now, let's simulate another situation: during employment, the person conducting the interview requires the candidate to provide a certificate of good conduct; a potential employee goes to the Government for Citizens corporation, takes a certificate and - bam! – his criminal record comes up, which was expunged 10-15 years ago. In such a situation, most citizens will not even go back to the employer, and those who overcome their fear and still go are unlikely to be hired. In most cases, the employer will not accept such an employee, choosing instead a person with a “clean” certificate of good conduct, indicating, however, a completely different reason for refusing the person a place. And what will a person do if he is not hired in the end? Should you sue, file a complaint with the state labor inspector or the prosecutor's office? But the chances of winning in such a case are very small, and even if he miraculously wins the trial, what kind of employer needs an employee who “sued” the boss even before getting a job?
What are the terms for expunging a criminal record?
According to Article 86 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, a person who has been released from punishment by the court upon issuing a guilty verdict is considered to have no criminal record and, accordingly, is not subject to restrictions. In other cases, the period for expunging a criminal record is determined depending on the severity of the punishment imposed by the court.
Question answer
How punishments for crimes differ in different countries of the world. Infographics
Thus, a criminal record is considered expunged:
a) in relation to persons on probation - after the expiration of the probationary period appointed by the court;
b) in relation to persons sentenced to more lenient punishments than imprisonment - after one year after serving or executing the sentence;
c) in relation to persons sentenced to imprisonment for crimes of minor or medium gravity - after three years after serving the sentence;
d) in relation to persons sentenced to imprisonment for serious crimes - after eight years after serving the sentence;
e) in relation to persons convicted of especially serious crimes - after ten years after serving the sentence.
If the court released the convicted person early from his sentence, or the part of the sentence that the citizen did not serve was replaced with a more lenient one, the period for expunging the criminal record is calculated based on the actually served term of the sentence from the moment of release from serving the main and additional types of punishment.
According to Article 95 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, for persons who committed crimes before reaching the age of 18, the terms for expunging a criminal record are reduced. They are equal:
a) six months after serving or executing a sentence less severe than imprisonment;
b) one year after serving imprisonment for a crime of minor or medium gravity;
c) three years after serving imprisonment for a serious or especially serious crime.
Question answer
Where do they require a certificate of no criminal record and how to get it?
If you are convicted, is it for life?
However, on July 10, 2014, the mentioned document lost force due to the adoption of a new order of the Prosecutor General of the Republic of Kazakhstan No. 71 “On approval of the Rules for maintaining and using certain types of special records.” This is where today’s problems with the employment of citizens arose, since paragraph 98 of the new order establishes that:
“The information contains information about the commission of crimes by the requested person, without taking into account their withdrawal and repayment, including information:
on implicating a person as an accused, convicting him, including outside the Republic of Kazakhstan;
on exemption from criminal liability and punishment on non-rehabilitative grounds;
about criminal cases initiated that were terminated on non-rehabilitative grounds;
on the refusal to initiate criminal cases on non-rehabilitative grounds..."
That is, the General Prosecutor's Office decided to reflect in the certificates of no criminal record all available specific information regarding all persons, regardless of whether the criminal record was cleared or expunged, whether the person was brought to criminal responsibility or was released on non-rehabilitative grounds. For example, an amnesty.
How to check your criminal record?
The possibility of obtaining information about the presence (absence) of a person of a criminal record (for example, when applying for a job in educational organizations or government agencies is provided for by the Administrative Regulations of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of Russia. As Kuleshov explains, information about a criminal record is stored in the Main Information and Analytical Center (GIAC) of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of Russia. Therefore You must submit an application there or to the information center of the territorial internal affairs body at your place of residence to receive the necessary information. If necessary, the application will be sent to prepare a certificate of territoriality. Now this certificate can be issued at the multifunctional center of public services.
The regulations also stipulate that applicants located outside of Russia receive the specified information through consular offices or consular departments of diplomatic missions of the Russian Federation, which receive information from the Main Information and Analytical Center of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Russian Federation.
Reflection of withdrawal information in the database
Info
Information about each prisoner must be reflected in a single database. The Main Directorate of the Ministry of Internal Affairs is in charge. Similar centers exist in every subject. The central source is the GIAC of the Ministry of Internal Affairs.
Even in a situation where the parties to the conflict have found a compromise and are reconciled, data on the violation is reflected in the database. The information indicates that the provisions of the criminal law were applied to the person, but he was not convicted.
Even in a situation where there was a domestic conflict with people living in the neighborhood, this falls into the database. The basis for this is the recording of information by employees of authorized bodies. It is provided that during the period specified in the law it will not be possible to remove this label of criminal record. Even if you move to another city, the information continues to be reflected in the standard manner.
If a citizen wants to have his criminal record expunged when applying to the court, he needs to understand that this is extremely difficult to do. The Ministry of Internal Affairs developed order No. 612 of 2007, which states that materials from criminal cases must be stored for a quarter of a century. Only certain employees of the Ministry of Internal Affairs receive permission to work with the base. For this reason, you will not be able to delete the information on your own.
There are several options for such removal:
- rendering a verdict of acquittal;
- if the data was entered into the database by mistake.
Attention
If an error occurs, the citizen is given the right to appeal to such authorities as the court or the prosecutor's office. You are required to make a written complaint and report that the database contains incorrect information.
What does early expungement of a criminal record mean and under what circumstances is it possible?
As Part 5 of Art. 86 of the Criminal Code, “if the convicted person behaved impeccably , then, at his request, the court may remove his criminal record before the expiration date of the criminal record,” if he personally petitions the court to remove his criminal record before the expiration of the expiration date. A criminal record can be expunged before the expiration of the period established by law not only by the court, but also by government authorities .
According to Part 2 of Art. 84 of the Criminal Code, persons who have served their sentence may have their criminal record expunged by an act of amnesty. The law also provides for the implementation of the same possibility through the pardon of a person who has served his sentence (Part 2 of Article 85 of the Criminal Code). In accordance with Part 1 of Art. 74 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, if before the expiration of the probationary period the conditionally convicted person has proven his correction by his behavior, the court, on the proposal of the body exercising control over the behavior of the conditionally convicted person, may decide to cancel the conditional sentence and remove the convicted person’s criminal record. In this case, the suspended sentence may be revoked after the expiration of at least half of the established probationary period. To do this, the body exercising control over the behavior of the conditionally convicted person must provide the following information about him: the conditionally convicted person Kukushkin, during the probationary period, fulfilled the duties assigned to him by the court and proved himself to be positive. Did not violate the terms of his probation. He promptly reported to the criminal-executive inspection about his behavior. Conscientiously fulfilled the duties assigned to him by the court. Did not allow the commission of administrative or other offenses. He reacted positively to preventive measures. At his place of residence, he is characterized on the positive side, and has proven his correction by his behavior.
Early removal of a criminal record by a court is equivalent to its expungement. Expungement or expungement of a criminal record cancels all legal consequences associated with a criminal record. In this case, not only the criminal law, but also all other legal consequences of the conviction are annulled, including restrictions that may be established for employment, etc.
Don't throw out the baby with the bathwater
The Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Republic of Kazakhstan and the Prosecutor General's Office of the country have finally seen this problem and are going to abolish police clearance certificates altogether, but this, in my opinion, is also not a way out of the current situation. After all, here you can, as they say, throw out the baby with the bathwater. That is, simply to open the way for persons who, by court, are deprived of the right for life to hold certain positions or perform certain duties due to their inconsistency with certain specific parameters necessary for the performance of such functions.
Meanwhile, today, when applying for a job, not all citizens must present a certificate of good conduct to the employer. Since individual articles of the Labor Code specify both the list of persons obliged to provide this document and the nature of the crimes that deprive them of access to certain functions. Thus, in accordance with paragraphs 2 and 3 of Article 32 of the Labor Code:
"2. To conclude an employment contract in the field of education, upbringing, organization of recreation and recreation, physical culture and sports, medical care, provision of social services, culture and art with the participation of minors, a person submits a certificate of the presence or absence of information about the commission of a criminal offense: murder, intentional infliction harm to health, against public health and morality, sexual integrity, extremist or terrorist crimes, human trafficking.
3. When entering the civil service, working in state-owned enterprises with the right of economic management, national management holdings, national development institutions, national holdings and national companies, as well as their subsidiaries for a position related to the performance of managerial functions, the person submits a certificate of the presence or absence of information about the commission of a corruption crime.”
Legal significance of a criminal record on the constitutional rights and freedoms of citizens
This article discusses the content and concept of a “criminal record,” its criminal legal meaning, expungement and expungement of a criminal record.
The Republic of Kazakhstan, declaring itself a democratic, secular, legal and social state, recognized in Article 77 of the Constitution one of the most important principles of the criminal process, the presumption of innocence. This means that our state and society consider a citizen to be conscientious or respectable until otherwise proven and legally established by an act of the judiciary [1].
The purpose of this scientific work is to consider the content and concept of a “criminal record ,” its criminal legal meaning, expungement and expungement of a criminal record.
Committing an act prohibited by the Criminal Code entails certain legal consequences. One of them is a criminal record. The definition of criminal record is the special position of a person in relation to the legal field, sentenced for committing a crime to a certain type of punishment and the period of its serving. And this is associated with the onset of certain legal consequences.
The object of the study is exemption from criminal liability and punishment.
The subject of study is the concept of a criminal record and its legal meaning, expungement and expungement of a criminal record.
In the works of Soviet legal scholars, a criminal record was viewed as a complex legal phenomenon, closely related to punishment - “a measure of state coercion applied by the court on behalf of the state to persons who have committed crimes, entailing certain deprivations or restriction of the rights of the convicted person and expressing on behalf of the Soviet state a negative assessment of the criminal and his deeds. Criminal punishment differs from other measures of state coercion in that its imposition always entails a criminal record” [2].
The institution of a criminal record is one of the most problematic links in the modern criminal justice of the post-Soviet countries, which is confirmed by the changes that the institution of repetition has undergone already during the existence of the new Criminal Code of the Republic of Kazakhstan.
The current Kazakh legislation does not define the purpose of the existence of the institution of a criminal record, which gives scope for interpretation of its features.
An explanation for this fact should be sought not only in the specifics of the current reform stage in the development of domestic criminal legislation, but also in the complexity of the problem underlying the interpretation of the category “criminal record”, the problem of criminal liability, including its beginning and termination. It is obvious that only fair punishment can achieve its goals, ensure effective correction, private and general prevention.
Russian experts testify that the existing regulatory framework regulating the institution of a criminal record in criminal law is insufficient.
In particular, Deputy Chairman of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation E. “has no criminal record” should be understood in relation to a person recommended for the position of an arbitration manager: some courts believe that the concept of a criminal record can be interpreted in this case in strict accordance with the understanding found in criminal law, other courts believe that the term “criminal record” should be understood in its broader meaning in comparison with its criminal legal content, as a fact of a person’s biography that has already occurred and can never be deleted from it [3].
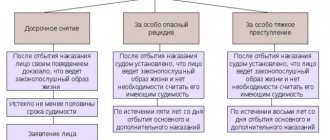
Options for terminating a criminal record: A person whose conviction has entered into force is considered to have a criminal record. The law establishes options for when a criminal record can be annulled early.
Expungement and expungement of a criminal record are the only two ways to terminate it. Removal of this type of punishment entails its termination before the legally established period for its repayment expires. All this is carried out on the basis of the relevant court decision. However, the law does not establish a minimum or maximum period after the expiration of which a criminal record can be expunged early.
Expungement and removal of a criminal record always occurs after serving the sentence established by a court decision in places of imprisonment. Or this is provided after the end of the suspended sentence. Expungement of a criminal record does not require a court decision. This happens automatically after the end of the period specified by law.
The deadlines are set taking into account the categories of illegal acts. There are situations in which the expungement or expungement of a criminal record entails consequences that are determined by the legal field. For example, a person who has been subjected to this type of punishment does not have the right to work in the police. A mandatory condition for expunging a criminal record is the end of the period of serving the sentence, regardless of what crime was committed. If a primary and additional punishment has been imposed, the start date for repayment begins after the end of the period of additional restraint. The expungement of a criminal record begins from the moment the sentence is served. This means from the moment of release, even if the criminal record was expunged early or the punishment was replaced with a more lenient preventive measure. The time during which the court sentence was not carried out due to reasons other than the convict’s evasion from serving the sentence is included in the period for expunging the criminal record. If for some reason the sentence was not carried out, then after the expiration of the limitation period the convicted person is considered not to have been convicted.
The difference between expungement and expungement of a criminal record. There are significant differences in the legislation in the procedure regulating the expungement and expungement of a criminal record. There is a difference between these concepts. It consists in the fact that the punishment is lifted by filing a petition with the court. This body gives a positive verdict on him. The second option is based on a document indicating that a decision on amnesty or pardon was made in relation to the person. Repayment occurs immediately after the end of the period established by law, depending on the degree of the act for which the conviction was assigned. Expungement and removal of a criminal record is impossible while serving a sentence. Is it possible to expunge a criminal record early? Early expungement of a criminal record is assigned to a convicted person before the end of the period of serving the sentence for impeccable behavior. What does it mean? Impeccable behavior is considered to be the absence of penalties, criminal offenses or administrative violations. To expunge a criminal record, you must file a petition. He is sent to court. This body reviews it and makes an appropriate decision. A positive court decision may be influenced by marriage, having a child, finding a permanent job, participating in charitable organizations, etc. Simply put, they take into account everything that can have a positive impact on the characteristics. Any person who has served his sentence, regardless of the degree of the crime, has the right to apply to have his criminal record expunged early. The removal of a criminal record early is not the responsibility of the court. Therefore, the person who has served his sentence and his defense attorney must prove their right to such a privilege. The expungement of a criminal record prematurely terminates the legal consequences that have arisen from the moment the preventive measure is determined (except for cases provided for by law). What to do if the court refuses? The convicted person has the right to submit a repeated petition no earlier than one year after the decision was made. Peculiarities of expunging a criminal record for minors Expunging a criminal record for minors (as opposed to adults) differs in terms of terms. That is, the period is shortened compared to the prescribed period for an adult citizen. For acts of minor and moderate gravity, the repayment period is one year. For especially serious crimes - three years. Convicted minors who have been sentenced to compulsory educational measures for crimes of moderate or minor gravity are considered unconvicted. If a more lenient punishment is established than imprisonment or a suspended sentence, then the criminal record in these situations is expunged at the end of the probationary period or after the expiration (after serving the sentence) of one year. Early expungement of a minor's criminal record is possible not only at the request of the convicted person.
This can be done at the request of his parents, guardianship and trusteeship authorities, as well as his legal representatives.
Conditional sentence: expungement of a suspended conviction can occur automatically or early. If the convicted person has proven by his behavior that he has reformed and compensated for the harm caused by the crime, the court may grant the petition. It is directed by a supervisory authority that monitors a person’s behavior. A decision may be made to cancel the suspended conviction and remove it from the convicted person. In this case, the expiration of a suspended conviction occurs after the expiration of 1/2 of the probationary period. There is no point in filing a petition before[4].
The time frame for expunging and expunging a criminal record depends on the category of crime: 1. After the end of a fifteen-year period from the date of serving a sentence for crimes of special gravity. 2. Expungement of convictions for serious crimes occurs after the end of ten years. 3. Acts of moderate and minor gravity require the expiration of a three-year period from the end of serving the sentence. 4. For milder types of punishment, the cancellation period begins after a year. 5. Conditionally convicted persons are released from their criminal record after a probationary period. A criminal record can be removed early only at the request of the convicted person. The day of the court decision is the moment of its early repayment[5]. Reasons for refusal: when considering a case on early removal of a sentence, the court has the right not to satisfy the petition of the convicted person and make a decision to refuse. The reasons may include the following criteria: 1. violation of the rules and norms of behavior established by law in places of deprivation of liberty. 2. relapse of crime. 3. lack of evidence of correction of the convicted person.
The legal significance of expunging a criminal record is that it completely cancels the legal consequences of a conviction. This means that from a legal point of view, a person is considered not to have committed a crime, not to have been prosecuted, not to have been punished and not to have served it[6].
The provision of a public service - the issuance of registration information available in relation to the applicant (certificate of the presence or absence of a criminal record) of the Republic of Kazakhstan was carried out by the Committee on Legal Statistics and Special Records under the General Prosecutor's Office of the Republic of Kazakhstan. In accordance with the Decree of the Government of the Republic of Kazakhstan dated 07/19/2008 “Issues of the Ministry of Justice of the Republic of Kazakhstan” and joint order dated 03/10/2009 No. 41 “On approval of the Rules for the interaction between the CSCs of the KRS of the Ministry of Justice of the Republic of Kazakhstan and the territorial departments of the KPSiSU under the State Prosecutorship of the Republic of Kazakhstan on issues of issuing a certificate about the presence or absence of a criminal record” is currently carried out on an alternative basis through Public Service Centers (PSC). In accordance with the decree of the Government of the Republic of Kazakhstan dated May 17, 2014, this public service became known as “Issuance of information on the presence or absence of information on the records of the Committee on Legal Statistics and Special Records under the General Prosecutor’s Office of the Republic of Kazakhstan on the commission of a crime by a person .
Requests are verified using an automated database and local registration file within a specified period of 6 days. Documents ready for issuance are transferred to the Public Service Center the day before the expiration of the issuance period specified in the receipt of the applicant on the day of receipt of the application in paper form, in open form. As can be seen from practice, in this procedure on the procedure for issuing the specified document, the constitutional rights of citizens to its confidentiality are completely violated. Therefore, it is proposed to issue a certificate of the presence or absence of a criminal record to the licensor in a sealed envelope. Another person who initiates the request is the employer. Therefore, when hiring citizens, the employer must, depending on the work provided, the position held and the category, compile a list of categories of workers, employees and officials for whom the law requires certificates of the presence or absence of a criminal record. Therefore, it is also suggested that in order to obtain this certificate, the employer must contact the Public Service Center through an electronic database. This, firstly, determines the categories of workers, employees and officials for whom, when hiring, a certificate of the presence or absence of a criminal record is required. In other cases, exclude the need for this certificate. Secondly, it will speed up the process of hiring citizens.
It is necessary to clarify that the previous procedure provided for, depending on the initiator of the request (citizen or government body), the issuance of different amounts of information about criminal records and criminal prosecution for the same person. State bodies and organizations authorized to carry out verification activities in relation to citizens were provided with information in accordance with the storage periods for information records provided for by the Rules, regardless of expungement, expungement of a criminal record or grounds for termination of criminal prosecution. “electronic government” web portal (egov.kz), the information was provided taking into account the expungement of a criminal record.
It should be noted that such changes in the issuance of these certificates occurred in accordance with Chapter 16 of the new Rules for maintaining and using certain types of special records, approved by order of the Prosecutor General of the Republic of Kazakhstan dated July 10, 2014 No. 71 (reg. No. 9638 dated July 29, 2014 of the Ministry of Justice of the Republic of Kazakhstan) .
According to these Rules, public services are provided to individuals by territorial bodies of the Committee on Legal Statistics and Special Accounts of the General Prosecutor's Office of the Republic of Kazakhstan, including through Public Service Centers or the “electronic government” web portal (egov .kz ). Information is issued in the form of an electronic document on paper. Now, regardless of the region of appeal, the information indicates all the information available to the Committee and its territorial bodies about the crimes committed by the requested person, as of the day of the inspection.
The information contains information about the commission of crimes by the requested person, without taking into account their withdrawal and repayment, including information:
- on implicating a person as an accused, convicting him, including outside the Republic of Kazakhstan;
- on exemption from criminal liability and punishment on non-rehabilitative grounds;
- about criminal cases initiated that were terminated on non-rehabilitative grounds;
- on refusal to initiate criminal cases on non-rehabilitative grounds.
The certificate itself now contains a warning that the information provided in the information is subject to use in accordance with current legislation, including in accordance with the deadlines for expunging and expunging a criminal record provided for by the relevant articles of the Criminal Code of the Republic of Kazakhstan.
In other words, the Prosecutor General’s Office now invites persons (for example, an employer or licensor) who review this required certificate to independently determine whether a citizen’s criminal record has been expunged or expunged, and, accordingly, whether there are legal grounds or consequences for the implementation of restrictions on his civil rights. I wonder how they will do this, given that information about this is not indicated in the certificate?
I consider this approach extremely ill-conceived for the following reasons: Firstly, in accordance with Article 79 of the Criminal Code of the Republic of Kazakhstan, a person released from punishment is recognized as having no criminal record. Expungement or expungement of a criminal record cancels all legal consequences associated with a criminal record.
A criminal record in accordance with criminal law is taken into account in cases of determining recidivism of crimes and when assigning punishment.
According to the Normative Resolution of the Supreme Court of the Republic of Kazakhstan dated October 19, 2001 No. 15 “On some issues of sentencing in the form of imprisonment”, a person who has not served a sentence due to release from it by a court verdict (decision), regardless of the length of stay in prison in connection with the election preventive measure in the form of arrest, is considered, in accordance with Part 2 of Article 77 of the Criminal Code, to have no criminal record from the moment the judicial act on the basis of which he is released from punishment comes into force. It is necessary to take into account the conditions specified in the law for expunging a criminal record. When a person is released from serving a sentence during its execution on the grounds specified in the General Part of the Criminal Code (on parole, amnesty, pardon, illness, replacement with a more lenient punishment), the procedure and terms for expunging a criminal record are calculated in accordance with Part 3, 4, Article 79 and Article 89 of the Criminal Code, if acts of amnesty or pardon do not provide for the removal of a criminal record.
If we turn to the current legislation, then a certificate of criminal record (presence or absence) is required when:
- concluding an employment contract in the field of education, upbringing, organization of recreation and recreation, physical education and sports, medical care, provision of social services, culture and art with the participation of minors;
- - admission to citizenship of the Republic of Kazakhstan;
- - registration of the procedure for the adoption of children;
- -entry into military service under a contract;
- -conscription for compulsory military service (citizens with a criminal record are not eligible);
- - when registering the procedure for accepting children into foster care;
- -to undergo training in the mediator training program and be included in the register of professional mediators;
- - when obtaining a license to engage in security activities;
- - when confirming the qualification requirements for carrying out the activities of private bailiffs;
- -state, “Issue of consent to acquire the status of a major participant in a bank or bank holding company” ;
- issuing permission to create an insurance (reinsurance) organization;
- issuance of a license, re-registration, issuance of duplicate licenses for the right to engage in notarial activities;
- issuing a license, re-registration, issuing duplicates of a license to practice law;
- to register for the purpose of carrying out the activities of a rehabilitation and (or) bankruptcy trustee and (or) an external surveillance administrator;
- nomination as a candidate for the President of the Republic of Kazakhstan, for deputies of the Parliament of the Republic of Kazakhstan, including on party lists, maslikhats, as well as a candidate for member of another local government body;
- other cases when government bodies represented by officials send so-called requirements for a criminal record (when considering candidates for civil service, law enforcement agencies, when licensing the issuance of a right to a weapon, etc.) , which indicate all criminal information, regardless from expungement, expungement of a criminal record or grounds for termination of criminal prosecution.
Secondly, the current legislation in the above cases literally establishes the requirement to present a certificate of the presence or absence of a criminal record. However, now the bodies of legal statistics and special records issue a completely different certificate about the presence or absence of information about the commission of crimes by a person. No changes have been made to legislative acts in this part, therefore the laws contain requirements for the provision of a criminal record certificate, but the authorized body no longer issues it; another certificate is issued instead.
Moreover, if we analyze the current legislation of the Republic of Kazakhstan, then a citizen’s existing criminal record (whether outstanding or expunged, expunged or not expunged) is the basis for restricting human rights in cases directly provided for in the laws (laws of the Republic of Kazakhstan “On Civil Service”, “On Law Enforcement Service” "). In other words, such a citizen will be denied employment in the civil service or law enforcement agencies, or when applying for a job in accordance with paragraph 3 of Article 26 of the Labor Code of the Republic of Kazakhstan. So why, for the sake of this case, provided for in paragraph 3 of Article 26 of the Labor Code of the Republic of Kazakhstan, did they change the Rules, since it would have been more expedient to provide for the employer’s requirement for a criminal record certificate from an authorized body, indicating information regardless of the expungement, expungement of a criminal record, or the grounds for termination of criminal prosecution?
In the vast majority of the above cases, an expunged or expunged criminal record should not be taken into account, and the citizen is considered and recognized as having no criminal record.
Thirdly, the presence of a citizen, in accordance with Article 79 of the new Criminal Code of the Republic of Kazakhstan, with an expunged or expunged criminal record, in my opinion, relates to the concept of personal secrets. It is necessary to take into account that authorized bodies have the right, in accordance with the Law of the Republic of Kazakhstan “On State Legal Statistics and Special Records” , to include information about citizens in the system of special records; for this, they are not required to consent to the use of information about them by a state body when solving problems included in his competence. Indicating in a certificate existing criminal information about a person without taking into account the provisions of the criminal law on expungement or expungement of a criminal record, not to mention any information about criminal prosecution, is not the competent task of the Committee. As far as I understand, the Committee was created to take into account such information, provide it in prescribed cases, and not simply disclose such information. In this case, the prosecutor's office must take effective measures to strictly observe the rule of law and protect the rights of citizens from excessive restrictions.
In our country, in everyday life, not every employer or official will understand and understand that a criminal record has been expunged or removed, that there was a legal basis for exemption from criminal liability, that there are no legal consequences. The reaction of any person to such a certificate is predictable; no one will want to get involved with a “previously convicted person” , because... Since Soviet times, this has been a “cliché” that limits a person’s basic rights guaranteed by law.
Therefore, in this matter it is necessary to respect the inviolability of private life and personal secrets, it is necessary to eliminate, and not create, any form of arbitrary interference in private life by the state. The right to privacy, like all human rights, is enshrined in the UN Charter. Article 8. The UN Universal Declaration of Human Rights states: “Everyone has the right to an effective remedy by competent national courts in cases of violation of his fundamental rights granted to him by the constitution or law” [7], in the European Convention for the Protection of Human Rights and Fundamental Freedoms , in the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights. The Constitution of the Republic of Kazakhstan also has a section dedicated to the inalienable rights of man and citizen in Article 18, which states that everyone has the right to privacy, personal and family secrets, and protection of their honor and dignity.
The rights and freedoms of man and citizen can be limited only by laws and only to the extent necessary in order to protect the constitutional system, protect public order, health and morals of the population. According to Article 16 of the Code of Criminal Procedure of the Republic of Kazakhstan, Article 10 of the Civil Code of the Republic of Kazakhstan and Article 18 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Republic of Kazakhstan, the private life of citizens, personal and family secrets are protected by law.
However, as we see, decisions of government bodies do not always correspond to the legal concept and are aimed at protecting the interests of citizens. These changes entail a deterioration in the situation of ordinary citizens who once had a criminal record, but through their work, behavior and attitude towards others have proven their correction and social role in society. Instead of providing assistance to such citizens, the state forces them to go to the courts and appeal against violations of their labor, social and civil rights due to the information indicated in the certificates about expunged or expunged convictions or criminal prosecutions [8].
Thus, by a guilty verdict of the Talgar District Court of the Almaty Region dated October 24, 2001. Citizen B. was convicted of committing a crime under paragraph “c” of Part 2 of Art. 175 of the Criminal Code of the Republic of Kazakhstan to 2 years of imprisonment, using Article 63 of the Criminal Code of the Republic of Kazakhstan, suspended with a probationary period of 1 year. According to the norms of the old “Criminal Code of the Republic of Kazakhstan” dated July 16, 1997 N 167-I, the new “Criminal Code of the Republic of Kazakhstan” dated July 3, 2014. No. 226-V, which entered into force on January 1, 2015, B.’s criminal record was expunged, but for 12 years his criminal record was not removed from the special register. Thus, according to paragraph 7 of Article 79 of the new Criminal Code of the Republic of Kazakhstan, if the convicted person behaved impeccably after serving his sentence, then, at his request, the court can remove his criminal record before the expiration date of the criminal record.
In July 2015 On legal grounds, he appealed to the Talgar District Court with a petition to have his criminal record removed. By the decision of the Talgar district court of Almaty region No. 4-158/15 of 2015. his request to have his criminal record expunged was unjustifiably denied. Thus, the court violated the constitutional rights of citizen B. to judicial protection of his rights, freedoms and legitimate interests (Article 13 of the Constitution of the Republic of Kazakhstan).
His direct appeal to the General Prosecutor's Office of the Republic of Kazakhstan for the removal of his criminal record did not yield positive results.
In connection with the above, I believe the resolution of the Government of the Republic of Kazakhstan dated May 17, 2014 and the order of the Prosecutor General of the Republic of Kazakhstan dated July 10, 2014 No. 71 (registration No. 9638 dated July 29, 2014 of the Ministry of Justice of the Republic of Kazakhstan), which approved the Rules for the maintenance and use of certain types of special records adopted in this part in violation of the norms of the Constitution of the Republic of Kazakhstan and the current criminal proceedings of the Republic of Kazakhstan, which clearly worsen the legal status of citizens and it is advisable, at a minimum, to return to the previous Rules for issuing certificates of criminal record, taking into account the expungement or expungement of a criminal record.
Used sources:
- kivvi.kz/search/constitution of the Republic of Kazakhstan 2015.
- Zeldov S. On the concept of criminal record // Jurisprudence. No. 1. P.61 – 69.
- Renov E. N. Texts of speeches at the All-Russian seminar-meeting “Changes in the anti-crisis management system in Russia in connection with administrative reform” . M., 2004. P. 119.
- GrosovaT. Criminal record: expungement and expungement of criminal record. Expungement and expungement of a criminal record: the difference. Criminal law of the Russian Federation. 22.01.
- Criminal Code of the Republic of Kazakhstan Almaty. Lawyer. 2015 .
- Minakov G. L. Criminal record and its legal consequences. Eagle,
- Universal Declaration of Human Rights un.org/ru/documents/decl_conv/…
- Erlan Erbolatuly, Kazakhstan League of Lawyers, 2012-2015. [email protected]