The chief accountant is a special position; he is the second person in the company after the manager. The chief accountant is responsible for the accuracy of accounting and tax accounting, and for the economy and finances of the company.
I think that all managers have long understood that the chief accountant must be a person not only of high professionalism and higher education, but also with the ability to think outside the box and solve complex problems. The level of responsibility of the chief accountant is as high as possible, because the chief accountant is responsible not only to business owners (financially and disciplinaryly), but also according to state laws (administrative, criminal and subsidiary liability).
Quite a lot has already been written about the responsibility of chief accountants to the management and owners of the company, so let's talk about responsibility to the state.
The legislative framework
Let's consider the legislative documents that regulate various forms of responsibility of the chief accountant:
- Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
- Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation (in particular, Article 15.11.).
- Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
- Federal Law No. 129 of November 21, 1996.
Let's consider the regulatory grounds for criminal prosecution of the chief accountant:
- Federal Law No. 309.
- Article 144 of the Code of Criminal Procedure.
Depending on the severity of the offense, the chief accountant can be brought to disciplinary, material, administrative, or criminal liability. Disciplinary action applies to all employees. They are not specific to chief accountants.
How to hold an employee to full financial responsibility ?
Violations by officials
The categories of offenses for which the company will be punished have been sorted out. Now let us outline the offenses for which penalties are provided for against officials.
All punishments can be divided into three categories:
- gross violation of accounting rules - we will consider separately;
- violation of deadlines or failure to submit accounting reports to the Federal Tax Service;
- failure to provide or untimely provision of accounting reports to Rosstat.
For failure to submit a balance sheet and its annexes, the responsible employee, for example the chief accountant, has the right to be fined in the amount of 300 to 500 rubles. Moreover, the standard for applying sanctions is different, despite the same size of the fine. For an outstanding balance, the Federal Tax Service applies the norms of Art. 15.6 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. In Rosstat - article 19.7 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. Moreover, the imposition of penalties does not relieve the responsible employee from the obligation to submit financial statements.
IMPORTANT!
The official whose duties include reporting to the Federal Tax Service and Rosstat will be fined. For example, for the chief accountant - if such responsibilities are specified in his job description. If the assignment of duties is not documented, a fine will be collected from the manager.
Controllers, before exacting liability for violations of accounting from an official, will request copies of documents. For example, the Federal Tax Service requires you to send a copy of the passport of the responsible employee, as well as attach a copy of the order of appointment to the position and job descriptions.
Material liability
The financial responsibility of the chief accountant can be of two forms:
- On a universal basis . Assumes MO on a general basis. If the chief accountant causes any damage to the organization, compensation equal to his average salary is recovered from him. For example, the damage to the company amounted to 100,000 rubles. The chief accountant's salary is 20,000 rubles. It will not be possible to collect more than 20 thousand from an employee.
- Full financial responsibility . Provides full compensation for damages. Let's consider a similar example: an organization suffered damage in the amount of 100,000 rubles. The chief accountant, if his guilt is proven, will have to pay compensation in the amount of 100,000 rubles, regardless of the size of his salary. The provision for full financial responsibility must be specified in the employment contract. It can only be delivered to employees with key positions (chief accountant, manager).
How to differentiate between the responsibilities of the manager and the chief accountant ?
IMPORTANT! If the employment contract does not contain a clause on full MO, the chief accountant will bear financial responsibility on a general basis.
You can oblige the chief accountant to pay compensation in the following cases:
- Lack of money or property.
- Damage to property (equipment, raw materials).
- Downtime due to the employee's fault.
- Fines assessed due to the fault of the chief accountant.
This is real damage. Compensation cannot be recovered for indirect damage (for example, lost company profits).
IMPORTANT! After discovering an offense, the manager must convene a special commission to identify the culprit. Only if the commission reveals that it is the chief accountant who is to blame can compensation be recovered from him. You also need to get an explanatory note from the employee.
Results
Bringing an accountant to subsidiary liability in the event of bankruptcy of an enterprise is becoming more and more realistic. Moreover, both in-house accountants and outsourced accountants can fall under this. To avoid being attracted to a subsidiary, you need to draw up a safe contract or job description, step back from making management decisions, keep records correctly and ensure the safety of documentation, and record any disagreement with illegal actions of management in writing.
Sources: Federal Law of October 26, 2002 No. 127-FZ “On Insolvency (Bankruptcy)”
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Administrative responsibility
The chief accountant will bear administrative responsibility for the following violations of the law:
- Accounting rules are not followed.
- The employee does not submit documents required for tax control within the established time limits.
- Registration deadlines are not met.
- The rules for carrying out operations with cash registers are ignored.
- The chief accountant violated the laws of the Russian Federation concerning the financial industry.
In 2021, amendments to Articles 15.11 and 4.5 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation came into force, concerning the procedure for bringing to justice. In particular, the following changes have been made:
- The amount of the fine has increased. Now it ranges from 5,000 to 10,000 rubles. The exact amount of penalties is determined by the court depending on the circumstances of the case.
- Responsibility for repeated violation of the law has been introduced. It will be valid if a new offense occurred during the previous administrative punishment. The fine in this case will range from 10 to 20 thousand rubles. An alternative option is disqualification of a specialist for up to 2 years.
- The statute of limitations for pending cases has been increased. Previously it was 3 months. That is, if the accountant’s offense was discovered after this time, it was impossible to hold the employee accountable. Now the period has been increased to 2 years.
- When establishing the guilt of the chief accountant, evidence of the misconduct must be presented. From 2021, you can use photo and video materials as such.
The illegal actions for which administrative liability is introduced were also specified:
- Registration of imaginary accounting items in registers.
- Introduction of accounts outside accounting registers.
- The reporting data does not correspond with the accounting registers.
All of these are quite serious violations.
Question: Is it possible in an agreement on full financial liability of the chief accountant to provide for liability for damage caused to the organization by dishonest performance of their duties? View answer
Who is responsible for tax evasion
According to the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation, the person who was authorized to generate and submit reports to the Federal Tax Service and/or actually perform the functions of a manager related to the payment of taxes and contributions should be responsible. If these duties and powers were officially assigned to the accountant, then he will have to answer (see Resolution of the Plenum of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation dated November 26, 2021 No. 48).
It will not be possible to evade responsibility even if the accountant quit at the time the violations were discovered and no longer works for the company.
In criminal law, there are two forms of guilt: intent and negligence.
Liability will arise if the investigator proves that the accountant acted with intent, for example, he deliberately prepared false reports and did not transfer the required amounts to the budget.
If a manager or chief accountant underpaid taxes through negligence, he cannot be held criminally liable (Resolution of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation of May 27, 2003 No. 9-P).
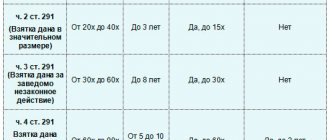
Criminal liability
The chief accountant bears criminal liability for offenses on the basis of Article 199.1 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation. According to the first part of this article, an official will be brought to the MA if the following factors are simultaneously present:
- The organization does not pay taxes in large quantities.
- The chief accountant commits illegal actions consciously.
- The violation of the law occurs for at least 3 years.
- The chief accountant, when committing illegal actions, is guided by his personal interests.
The second part of Article 199 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation is also of interest. It talks about exemption from the UO in the following circumstances:
- The offense was completely for the first time.
- The company has made all required payments to the country's budget.
The rules under consideration are relevant not only for chief accountants, but also for other officials who are responsible for paying taxes.
Is it possible to assign full financial responsibility to an employee to whom the powers of the chief accountant are transferred?
How an accountant can protect himself
The main question is how the chief accountant can avoid subsidiary liability. To answer this question, it is necessary to understand on what grounds an accountant is most often hired as a subsidiary.
Firstly, this is distorted information presented in accounting documents or the absence of these documents. Namely, an accountant, in-house or outsourced, conducts accounting and is responsible for the correctness and availability of all primary documentation.
The second reason for involvement is the chief accountant receiving some “goodies” from the company’s management for committing illegal actions.
From this we can conclude how to protect the chief accountant from subsidiary liability. First of all, reliably maintain the company’s accounting and tax records. It is dangerous to create fictitious document flow, hide company assets, conduct transactions with shell companies and technical companies, and distort the organization’s reporting.
It is clear that this sounds good in words, but many managers and owners have completely different goals. Therefore, the accountant should make every effort to minimize his risks.
It is impossible to create an outsourcer agreement or a job description for a chief accountant without subsidiary liability, since the provisions of federal law are primary compared to the provisions of the contract. But you can draw up a job description or contract in such a way that there are fewer reasons for attracting a subsidiary.
And, of course, you should not work with organizations where violations are obvious and predictably will lead to bankruptcy. If you assist management in this or even simply turn a blind eye to violations, then there is a high probability of being attracted to a subsidiary.
Read about liability for tax offenses in our selection “Tax liability for non-payment of taxes in 2020-2021 ” .
Is it possible to hold the chief accountant accountable after his dismissal?
If wrongdoing is discovered after an employee has been fired, they can still be held accountable. To do this you will need to go to court. The statement of claim must be filed within 12 months from the date of discovery of the offense. The task of the manager in court is to collect evidence that the chief accountant caused real damage to the organization. Lost profits do not fall into the category of real damage.
IMPORTANT! 12 months must be counted from the date the offense was discovered, and not from the date it was committed. It is advisable to take care of evidence that a violation of the law was detected on a certain day.
How to attract a chief accountant in practice
Since 2021, the subsidiary liability of the chief accountant has become a reality. Previously, it was mainly directors who were involved in subsidiaries. In connection with amendments to Law No. 127-FZ, which we have already mentioned, the chief accountant bears subsidiary liability in bankruptcy. This is not yet the most common practice, but there are already cases where an accountant is held vicariously liable.
We wrote about the rights and responsibilities of an accountant here .
Let us give examples from judicial practice on the subsidiary liability of the chief accountant.
Resolution of the Arbitration Court of the West Siberian District dated September 23, 2019 No. F04-1603/2019
The chief accountant and the head of the legal department for bankruptcy of the bank were brought to subsidiary liability. The case went to cassation. According to the judges, the defendants took part in approving the unprofitable transaction, although the final decision on it was made by the board of directors.
Resolution of the Arbitration Court of the Moscow District dated August 1, 2019 No. F05-5515/2018
The chief accountant was brought to subsidiary liability, as his conspiracy with the head of the company was proven, which led to the infringement of the rights of creditors.
Case No. A40-33003/17-88-45 “B”
An accounting firm was brought to subsidiary liability for distorting accounting and reporting data, errors in accounting and violations of legal requirements.
An outsourced accountant is subject to subsidiary liability on the same basis as a full-time accountant.
Sign up for a free trial access to ConsultantPlus and get acquainted with interesting examples from judicial practice on bringing to subsidiary liability. Even CDL children can be involved in the subsidy.
Responsibility of the chief accountant for non-payment of salaries to employees
Non-payment of wages is a serious offense for which not only the manager, but also the chief accountant is responsible. An employee who has not received the required funds has grounds to contact the Labor Inspectorate. After this request, checks are initiated in the organization. If violations are identified during the inspection, fines are issued. A specific person, including the chief accountant, can be required to pay a fine. Let's look at who exactly will be responsible:
- If the salary was not paid due to the fact that there are no funds in the organization’s account, responsibility rests with the head of the enterprise.
- If there are funds in the account, this is considered evidence of delay of money due to the fault of the chief accountant. Accordingly, he will bear responsibility.
In this case, administrative liability is usually imposed in the form of a fine.
How to recognize negligence
Carelessness can be careless and thoughtless.
If the accountant did not know that his actions could result in non-payment of taxes, then he acted negligently.
And if the accountant knew that he was committing a violation, but hoped to prevent it, then he acted frivolously.
If the accountant or the head of the company realized that they were hiding income in order to avoid paying taxes, but continued to do it anyway, then they acted intentionally.
New employee
By the time the chief accountant prepares to leave his position, it is important for the director to find a person capable of holding this position. Doing this when the chief accountant has already left is highly not recommended if there is an objective opportunity to find a specialist in advance. Without a new employee on staff, the old chief accountant will not be able to transfer matters to him, and he, in turn, will have to independently deal with the current documentation. This state of affairs is fraught with the possibility of making annoying mistakes in work, for which the new chief accountant most likely will not be to blame, because no one prepared him. We have heard so many stories from our colleagues when the new chief accountant had to work 11-12 hours a day for several months just to sort out all the paperwork. We recommend that directors be more humane in this matter and not create additional problems.
Moreover, it is important to note here that the new employee has every right to demand that the old chief accountant provide documents from previous reporting periods in order to check them for errors. He also has the right to report any shortcomings to his immediate superior - the general director.
Limitation periods
Criminal liability of an accountant occurs even when tax authorities no longer have the right to collect taxes. This circumstance is due to the fact that inspectors can conduct an inspection for a period of no more than 3 years. A Art. 78 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation provides that a criminal case can be initiated:
- After 2 years - for minor crimes.
- After 6 years – for crimes of medium gravity.
- After 10 years – for serious crimes.
Thus, in the second and third cases, the period of bringing accountants to criminal liability is significantly longer than the period of eligible tax audits.
It should also be taken into account that a conviction of an accountant does not cancel the collection of arrears of taxes and fees. They can be repaid both at the expense of the organization and at the expense of the person who is brought to criminal liability. Currently, the number of such cases involving double jeopardy is constantly increasing.
Responsibilities and role
A position that requires business skills is, without a doubt, a vacancy in the financial sector.
The chief accountant takes part in almost every meeting at which further prospects for the development of the company are discussed.
His position is associated with the implementation of absolutely all material transactions. Applicants for this position are subject to strict requirements for both personal qualities and education.
The work of the department and its relationship with the director is carried out in accordance with the Federal Law of the Russian Federation “On Accounting” dated December 6, 2011, as amended.
It provides a legal mechanism for activities, as well as the establishment of general requirements.
The action applies to the following bodies:
- institutions of all forms of ownership;
- government departments;
- Central bank;
- entrepreneurs and those engaged in private practice;
- branches of foreign companies located on the territory of the Russian Federation.
Another important element of activity is the relationship with creditors and debtors. The strategy for maintaining these relationships by the manager must be planned in advance with the mandatory involvement of accounting. He has complete data on the state of the organization, and thanks to correct analysis he will be able to predict the amount of income and expenses.
The role of the financier is high when interacting with government bodies that monitor compliance with laws. When conducting an inspection, the success of its implementation will depend on him. In these situations, he will be required not only to show a complete picture of financial and economic activities in accordance with regulations, but also to demonstrate a good level of business communication and etiquette.
In other words, with poor communication skills you can fail the inspection, even taking into account the fact that the information required by the regulatory authorities is compiled correctly. This situation may arise due to the fact that the regulatory framework is very extensive and seemingly identical things can be interpreted differently.
Introductory information
To begin with, let us recall that the relationship between the employer and the accountant is regulated by labor legislation.
Therefore, the responsibilities of an accountant (like other employees) are determined, first of all, by an employment contract and are specified in the job description. The position of an accountant itself does not yet imply performing “by default” everything related, for example, to cash flows. In this regard, we recommend that you re-read your employment contract and your job description. The risks of being brought to various types of liability directly depend on the content of these documents. Draw up and print an employment contract
“Goodbye” they said to the Chief Accountant
The dismissal of the chief accountant may take on a less “voluntary” nature when it comes to systematic violations of discipline, as well as a whole list of other acts aimed at causing harm to the company. As an example, here are some of them:
- Regular lateness to work can be regarded as a violation of discipline, and therefore the internal regulations established in the company;
- Errors in reporting made by the chief accountant personally or by his subordinates, which subsequently resulted in the imposition of significant fines on the organization;
- Loss of primary documents and irresponsible attitude towards their restoration. He is in charge of storing these and many other papers;
- Implementation of fraudulent schemes related to the transfer of funds to unreliable counterparties without the knowledge of the director;
- Endorsement of invoices without the knowledge of the manager in the absence of the right to sign.
This list can be continued for a long time. It is important to understand that the chief accountant is in charge of all the affairs of the organization. Plus, he has a complete understanding of its business activities. Any action that causes material damage can ultimately turn out sadly for the chief accountant. Unfortunately, when hiring any employee, it is impossible to know 100% for sure how cooperation with him may turn out. Here it’s only according to Stanislavsky: “I believe” or “I don’t believe.”